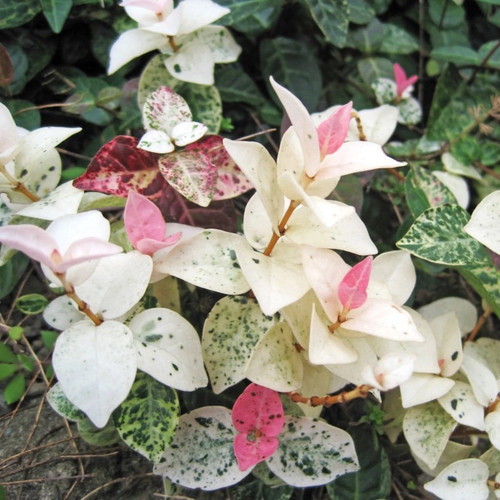
Jasmine
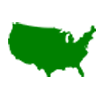
Growing Zones 7-10
Partial Shade to Full Sun
Great For Containers
Strongly Scented Flowers
Why We Love Jasmine
About Jasmine

ICommon Jasmine, Poet's Jasmine, White Jasmine, Jasmine Vine
Europe, Asia, and North Africa.
Bushes
Evergreen
7 to 10
White, yellow, pink, or purple
Jasmine typically blooms from spring to summer, though some species bloom year-round, depending on the growing environment.
Depending on the species, Jasmine can grow as a shrub, vine, or ground cover. Some are climbing or sprawling.
Pollinators, especially bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds
Drought, salt, pollution, and poor soils
Jasmine plants can resist some pests but are prone to aphids and spider mites in warmer climates.
How To Use Jasmine In The Garden
Jasmine plants are renowned for their sweetly scented pink or white flowers, which bloom in late winter or spring, depending on the variety. Species like Star Jasmine, Asiatic Jasmine, and Arabian Jasmine feature twining vines capable of covering structures with fragrant blooms. Some varieties are shrubby and can be pruned into formal shapes or cultivated as ground covers.
Vining types can adorn trellises, fences, or arbors, adding a tropical aesthetic to outdoor spaces. Shrubby forms of common white jasmine and winter jasmine are suitable for shaping or using as ground covers, providing versatility in landscape design. When planted in containers, jasmine can enhance porches or balconies with its delightful fragrance.
Jasmine Care
Plant Jasmine in full to partial sun exposure to promote prolific growth and blooming. It prefers rich, loamy soil with good drainage and a neutral to slightly alkaline pH. Regular watering is essential to keep the soil consistently moist but not oversaturated; increase frequency during dry periods. Applying a balanced, slow-release fertilizer each spring supports healthy growth.
Regular pruning after flowering helps maintain a neat appearance and encourages a dense form. Remove overgrown, damaged, or dead branches to promote vigorous growth. In colder climates, protect outdoor jasmine by wrapping the plant in landscape fabric and applying a thick layer of mulch over the roots. When growing jasmine in containers, use a rich, well-drained potting mix and place the pot in full sun to partial shade, watering when the top few inches of the potting mix are dry.
Learn More About Jasmine Care

Jasmine Companion Plants
Companions should like the same recipe of quick‑draining soil, a solid six hours of sun, and only light feeding that suits jasmine’s lean, Mediterranean rhythm. Gardenia forms a glossy evergreen screen through which jasmine can thread, while compact lavender anchors the base with drought‑tolerant silver foliage and summer spikes. Higher up the support, clematis extends the floral calendar once jasmine wanes, and lantana brings continuous color without being overwhelmed by other robust growers.